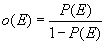
Odds
Gerard E. Dallal, Ph.D.
The odds o(E) of an event E is the ratio of the probability that the event will occur, P(E), to the probability that it won't, 1-P(E), that is,
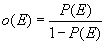
For example, if the probability of an event is 0.20, the odds are 0.20/0.80 = 0.25.
In epidemiology, odds are usually expressed as a single number, such as the 0.25 of the last paragraph. Outside of epidemiology, odds are often expressed as the ratio of two integers--2:8 (read "2 to 8") or 1:4. If the event is less likely to occur than not, it is common to hear the odds stated with the larger number first and the word "against" appended, as in "4 to 1 against".
When the odds of an event are expressed as X:Y, an individual should be willing to lose X if the event does not occur in order to win Y if it does. When the odds are 1:4, an individual should be willing to lose $1 if the event does not occur in order to win $4 if it does.
A common research question is whether two groups have the same probability of contracting a diseaase. One way to summarize the information is the relative risk--the ratio of the two probabilities. For example, in 1999, He and his colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine that the realative risk of coronary heart disease for those exposed to second hand smoke is 1.25--those exposed to second hand smoke are 25% more likely to develop CHD.
As we've already seen, when sampling is performed with the totals of the disease categories fixed, we can't estimate the probability that either exposure category gets the disease. Yet, the medical literature is filled with reports of case-sontrol studies where the investigators do just that--examine a specified number of subjects with the diesease and a number without it. In the case of rare diseases this is about all you can do. Otherwise, thousands of individuals would have to be studied to find that one rare case. The reason for the popularity of the case control study is that, thanks to a little bit of algbera, odds ratios give us something almost as good as the relative risk. allow us to obtain something almost as good as a relative risk.
There are two odds ratios. The disease odds ratio (or risk odds ratio) is the ratio of (the odds of disease for those with some exposure) to (the odds of disease for those without the exposure). The exposure odds ratio is ratio of (the odds of exposure for those with disease) to (the odds of exposure for those without disease).
When sampling is performed with the totals of the disease categories fixed, we can always estimate the exposure odds ratio. Simple algebra shows that the exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio! Therefore, sampling with the totals of the disease categories fixed allows us to determine whether two groups have different probabilities of having a disease.
A bit more simple algebra shows that if the disease is rare (<5%),
then the odds of contracting the disease is almost equal to the
probability of contracting it. For example, for p=0.05,
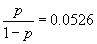 , which is not much different
from 0.05. Therefore, when a disease is rare, the exposure odds ratio is
equal to the disease odds ratio, which, in turn, is approximately equal
to the relative risk!
, which is not much different
from 0.05. Therefore, when a disease is rare, the exposure odds ratio is
equal to the disease odds ratio, which, in turn, is approximately equal
to the relative risk!